搜索引擎 为 Rails 项目升级使用 ElasticSearch 5.x 版本
最近为项目系统中使用的 Elasticsearch 进行了升级。从原来 1.4 版本的 Elasticsearch 升级到 5.x 版本。
由于 5.x 版本的 Elasticsearch 不再支持 1.4 版本中的很多查询语法,所以不可避免的进行了查询层的重构。
每次 Elasticsearch 有重大版本升级的时候,会在官方文档中列出相应的改变,你需要认真阅读的Breaking changes内容。
最重要的事情是,终于可以利用这次机会,为 Elasticsearch 加入了索引别名机制
安装
Elasticsearch-5.x server 版本的安装可以参考之前的博文。我是安装在 Ubuntu16.04 上,Ubuntu14.04 也是可以的。
在Gemfile中增加
gem "elasticsearch"
gem "elasticsearch-model"
gem "elasticsearch-rails"
使用最新的 elasticsearch gem 包,至少大于 5.0 版本
加入索引别名机制
为什么说别名机制是最重要的事情呢?我们知道 Elasticsearch 的索引,当你配置并建立好之后,是无法进行更新修改的。 想要进行更新修改,需要删除原来的整个索引,然后再根据新的配置,重建索引,包括索引的文档数据。这就不可避免了该索引在重建过程中 有一段时间是不可用的。
举个简单的例子:Elasticsearch 有一个 orders 索引,大概有 1000w 条记录数据。你的客户会经常使用查询 orders 的功能,这个功能查的就是 orders 索引。
现在你要修改 orders 索引的分词器。这时你需要重建 orders 索引 (删除再新建),假设这个过程,让 orders 索引完全恢复到可用状态需要 10 分钟。那么,你的客户就会
有 10 分钟没法使用 orders 的搜索功能。当然,你可以在凌晨 3 点进行这个操作。这里只是举个例子。Elasticsearch 索引别名机制可以帮助你进行索引无缝的升级或更新。
别名机制的过程及原理
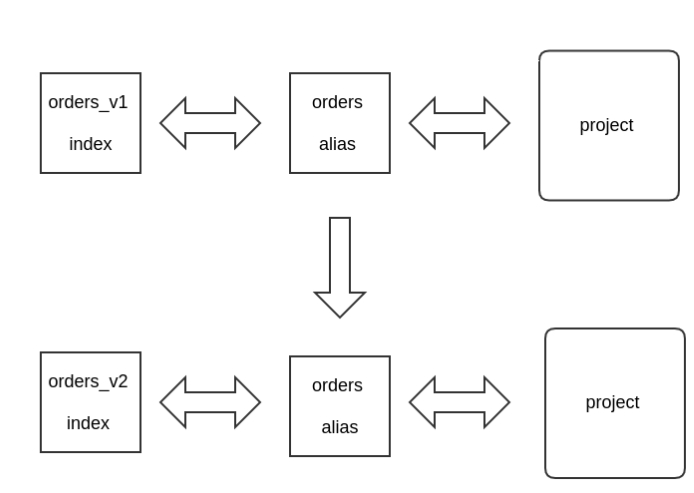
关键的操作是:取别名。现在我要重构 orders 这个索引,我会先创建一个叫做 orders_v1 的索引,为其配置名称为 orders 的别名。
这样,在查询代码层,你就可以使用类似Order.__elasticsearch__.search()这样的查询了。其实,也就是 在代码层面上,不知道有 orders_v1 这个索引额存在,
一切对 Elasticsearch 的操作,都通过别名 orders 操作。
现在,我们需要修改 orders_v1 索引,只要简单的三步:
- 1. 用新的索引配置新建一个叫 orders_v2 的索引,将文档数据也建立好
- 2. 进行切换别名的操作,将 orders 别名由原来 order_v1 指向 orders_v2
- 3. 看你的需要,再进行增量变更数据的更新
切换别名的操作非常快,并且你的代码层的修改会变得很轻松。几乎不会对用户的使用造成影响。
简单的图表示:
在项目中,实现别名机制不难。详见官方文档的例子
新建索引别名
POST /_aliases
{
"actions" : [
{ "add" : { "index" : "order_v1", "alias" : "orders" } }
]
}
切换索引别名
POST /_aliases
{
"actions" : [
{ "remove" : { "index" : "order_v1", "alias" : "orders" } },
{ "add" : { "index" : "order_v2", "alias" : "orders" } }
]
}
在 rails 项目中,我通过 rake 脚本实现,下面是我写的一个 rake 脚本,在新建或重建索引的时候使用,仅供参考。
#coding: utf-8
client = Elasticsearch::Client.new(
host: elasticsearch_url,
retry_on_failure: 0,
log: true,
transport_options: { request: { timeout: 10 } }
)
# ++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++使用方式++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
#1 创建索引 # bundle exec rake es_action:create_index table=Order index_name=orders_v1
#2 索引别名配置 # bundle exec rake es_action:update_index_alias alias=orders new_index=orders_v1 old_index=orders_v2(可选,交换索引的时候使用)
namespace :es_action do
desc "重建es索引,根据传入的参数指定重置的索引"
task create_index: :environment do
table = ENV['table']
index_name = ENV['index_name']
puts "++++++ start remapping index #{table}"
if table.blank? || index_name.blank?
puts "table 和 index_name 参数不能为空"
return
end
model = table.camelize.constantize
model.__elasticsearch__.create_index! index: index_name, force: true # ++++++创建索引
model.__elasticsearch__.refresh_index! index: index_name
end
desc "新建或交换es的别名(将别名由旧的索引指向新的索引)"
task update_index_alias: :environment do
old_index = ENV['old_index']
new_index = ENV['new_index']
alias_name = ENV['alias']
puts "++++++ start update_index_alias #{alias_name}"
if alias_name.blank? || new_index.blank?
puts "++++++ alias new_index 参数不能为空"
return
end
body = {actions: []}
body[:actions] << {remove: {index: old_index, alias: alias_name}} if old_index.present? # old_index存在,表示是进行别名切换
body[:actions] << {add: {index: new_index, alias: alias_name}}
client.indices.update_aliases body: body
puts "++++++ update_index_alias success"
end
end
mapping 的配置
app/models/order.rb
1.4 版本中的 mapping 配置
indexes :subject, type: 'multi_field' do
indexes :raw, type: :string, index: :not_analyzed
indexes :tokenized, analyzer: :ik_smart
end
indexes uuid, type: :string
indexes amount, type: :integer
indexes price, type: :long
indexes :created_at, type: :date
indexes :updated_at, type: :date
indexes :users do
indexes :id, type: :integer
indexes :name, type: :string, index: :not_analyzed
end
5.x 版本中的 mapping 配置
indexes :subject, type: :keyword do
indexes :raw, type: :keyword
indexes :tokenized, analyzer: :ik_smart
end
indexes uuid, type: :text
indexes amount, type: :integer
indexes price, type: :long
indexes :created_at, type: :date
indexes :updated_at, type: :date
indexes :users do
indexes :id, type: :integer
indexes :name, type: :keyword
end
5.x 版本没有了 string 类型,拆分成了 keyword 和 text。如果你指定了 analyzer,则是 text 类型;如果指定了 text 类型但是没有指定 analyzer,则会使用默认的 analyzer
不再有 type: 'multi_field',这个好像是 2.x 版本就废弃了
5.x 的 IK 也分成了两种配置。
ik_smart和ik_max_word,ik_max_word拥有更细的分词粒度。
查询语句的重构
修改例子:
不再使用 filtered
{filtered: {
filter: {
bool: {
must: [{or: [{terms: {user_id: user_id}}]},
{term: {order_id: order_id}}
],
}
}
}
}
# 重构为:
{bool: {
filter: {
{bool: {
must:[
{term: {order_id: order_id}},
],
should: [
{terms: {user_id: user_id}}
]
}
}
}
}
}
不再使用 or
filters[:must] << {
or: [
{term: {order_id: order_id}},
{term: {user_id: user_id}}
]
}
#重构为:
filters[:must] << {
bool: {
should: [
{term: {order_id: order_id}},
{term: {user_id: user_id}}
]
}
}
不再使用 missing
{missing: {field: field_name}}
#重构为:
{"bool": {
"must_not": [
{
"exists":{
"field": field_name
}
}
]
}
}
execution: 'and'不再使用
{terms: {field_name => value, execution: "and"}}
#重构为:
terms_array = value.map {|v| {term: {field_name => v}}}
{bool: {must: terms_array}}
Elasticsearch 的功能还是很强大的,这次 Elasticsearch 升级没有使用自定义的 Routing 的机制,一个是任务时间考虑,另一个是现在的服务负载还能撑一段时间,并不急迫需求这样的优化。现在有了索引别名,以后就可以放心的考虑优化进程了~